Quantitative Electroencephalography (QEEG)
What is QEEG Brain Mapping?
Quantitative Electroencephalography or QEEG is an assessment that measures the brain's bioelectrical activity and quantifies it by comparing it to a normative database in order to determine the underlying causes of the presenting symptoms. The QEEG can be an invaluable tool in determining what is happening diagnostically in the brain. It can reveal if the client has a sleep disorder, ADHD, Depression, Anxiety, OCD, PTSD, Autism Spectrum Disorder, among other relevant diagnostic considerations.
Emotion and EEG Frequency Outcomes
Delta 0.5-4 hz (cycles/second) - associated with sleep
Theta 4-8 hz - dream like state, reflective, creative inward thought
Alpha 8-12 hz - “in the now” focus, an alert relaxation
Low Beta 12-15 hz (SMR located in sensory motor strip) - mind/body calmness
Beta 15-20 hz - mental alertness, processing, analytical
High Beta 20-30+ hz - over-active brain, anxiety, obsessive or racing thoughts, panic, etc…
How is the QEEG Administered?
The process entails placing nineteen non-invasive EEG sensors onto the scalp and taking two recordings (eyes open and eyes closed). The recordings are then reviewed by a neurologist and a QEEG expert, who review the raw EEG and compare the findings to a normative database. By assessing where the client's brainwave activity is functioning outside of the norms, we can then develop an individualized neurofeedback treatment protocol in order to train the brain to function in a more optimal way. With the change in the bioelectrical activity, clients often experience a reduction in symptoms.
The QEEG is done in person in the comfort and convenience of our office.
Why is a QEEG Recommended?
The QEEG is an invaluable tool in rooting out the bioelectrical causes of mood dis-regulation, poor mental performance, and behavioral problems. While many issues can present with the same symptoms, the underlying brain pattern can differ greatly from person to person. There are NFB practitioners who will forego the QEEG in favor of a symptom based approach. This approach focuses on training the areas of the brain that are most commonly associated with various symptoms, and has yielded positive results.
For example, it's been observed that patients who present with ADHD symptoms typically have an excess of slow-wave activity at the vertex and in the frontal part of the brain. A typical symptom-based protocol would involve training those areas to inhibit the slow-wave activity. However, every brain is different and the QEEG could provide more specific protocols for greater effectiveness. Using the same example, a patient with ADHD may have an underlying seizure disorder, which may be causing the symptoms, and by training to increase the beta frequency (commonly associated with focus), one could exacerbate the seizure-like activity. The QEEG also provides a concrete measure of the changes that occur in the brain after training has occurred.
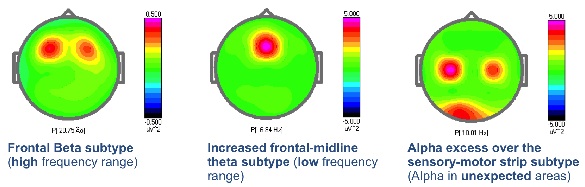
Example of three different ways that ADHD can manifest in the brain. Each pattern can be more effectively treated with neurofeedback protocols that are targeted to train the affected areas.
QEEG for Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Detection in Athletes: A Rising Awareness
With increasing awareness of the long-term impacts of traumatic brain injuries (TBI) on athletes, the importance of comprehensive brain health checks cannot be overstated. Repetitive TBIs, often linked to contact sports, can result in chronic symptoms such as headaches, memory and concentration difficulties, mood changes, balance issues, and sleep disturbances. Over time, these symptoms may affect an athlete's performance, decision-making skills, and overall well-being. Furthermore, repetitive TBI carries a risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases later in life, such as chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), Alzheimer's disease, or Parkinson's disease.
The QEEG, through its detailed mapping of brainwave activity, plays a vital role in identifying changes and irregularities often associated with TBI. These insights offer critical guidance for tailoring treatment strategies and managing the athlete's safe return to play. In an era of heightened awareness, tools like the QEEG are invaluable in safeguarding athletes' well-being while aiding them in their pursuit of peak performance.